What Are Electrical Insulators?
An electrical insulator is a component which does not allow the electric current. Just imagine how important insulation is in our daily lives?
Insulation protects humans from getting electrocuted. The wire carries electricity to your computer with an insulating material that protects you. Good insulators include glass, air, paper, rubber, and mica. in this article,
we discuss different types of insulators that exist in a market which used in transmission and distribution. The purpose of the insulator is to provide support to the overhead line conductors and stop the current flow towards the earth.
In this article, we will discuss types of insulators, different types of insulating materials, the relation between moisture And insulation, and how we protect electrical insulation against moisture.
General Properties of insulating material
- The dielectric strength of the insulating material must be high.
- it Material insulating resistance should be high.
- Thermal expansion of the insulating Material must be minimal.
- The insulator Material must be non-ignitable.
- The thermal strength of the insulating material must be high.
- The mechanical strength of the insulators is high.
 |
| Dielectric strength of different materials |
Types of Electrical Insulators
In this article, we discuss the most common types of insulators that are used for transmission and distribution purposes which including
- pin type insulator
- post type insulator
- suspension insulator
- shackle insulator
- Hollow insulators
- porcelain insulators
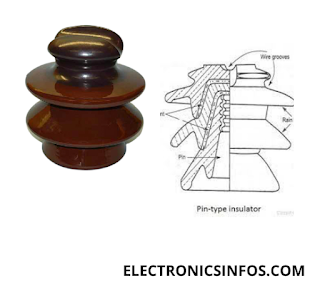
Pin Type Insulators
Pin-type insulators are essential components in electrical systems, particularly for overhead transmission lines. it is made from materials like porcelain or glass, which are excellent insulators.
This design often includes rain sheds or petticoats, which serve the dual purpose of increasing the creepage distance and protecting the insulator from rain.
The pin insulator has grooves on the top side to support the conductor. There are two sides of the groove: the first on the top side is in a straight line position and the second side groove is in an angle position.
 |
| Pin Type Insulators |
Materials of pin-type insulator
- porcelain
- polymer
- ceramic
- silicon rubber
Range of pin type insulator
up to 33 kV systemApplications of pin-type insulator
- They are commonly used to support and separate electrical conductors on utility poles and transmission towers.
- Pin-type insulators can be found in substations where they isolate high-voltage conductors from the ground.
- These insulators are also used in the electrification of railway networks.
- They are suitable for medium to high-voltage applications.
- Pin-type insulators provide high mechanical strength.
post-type insulator
post-type insulators have a comparatively higher number of sheds as compared to pin-type insulators. post insulator is a high-voltage insulator design based on ANSI, IEEE and other standards. The mechanical strength of post-type insulators is high so we used them in distribution and transmission lines.
Types of post-type insulator w.r.t Design
- tie top-line posts
- horizontal clamp top-line posts
- horizontal (gain base) line posts
- brace post insulators
- vertical clamp top-line posts
Materials of post-type insulator
- plastic
- polyvinyl-chloride
- porcelain
- glass
- ceramic
Range of post-type insulator
11 kV to 765 kVApplications of Post-type insulator
- Post-type insulators are used in high-voltage power systems up to 1100 kV.
- it is also known as line post insulators in Transmission and distribution lines.
- it is used as a Supporting conductor in both horizontal and vertical installations on utility poles.
- They are preferred for their excellent mechanical properties.
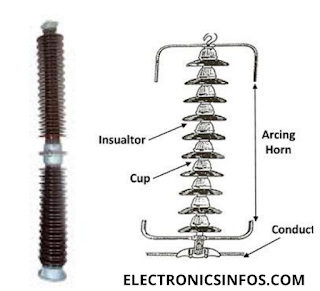
suspension insulator
There are two parts of a suspension insulator: One part is the insulator's arm and the other part is the cross arm. suspension type insulator protects an over-headed transmission line. This insulator is highly flexible because The string is free to swing in any direction. The suspension insulator is flexible so that easily be replaced with a new unit. we connect suspension-type insulators in series to enhance the power of the insulation in high-voltage applications.
 |
| suspension insulator |
Materials of suspension Insulator
porcelain materialRange of Suspension Insulator
>11KvApplications of Suspension insulator
- Suspension insulators are used in high-voltage transmission lines to support overhead conductors.
- Suspension insulators are also used in substation equipment such as circuit breakers, transformers, and busbars.
- In railway electrification systems, suspension insulators are used to support overhead catenary wires.
- Suspension insulators find application in distribution lines for medium and low-voltage electricity distribution.
- Suspension insulators are utilized in telecommunication towers to support antennas and transmission lines.
Shackle insulator
A shackle insulator is a low-voltage insulator that is used in distribution circuits. we also called the spool insulator. There are two positions of this insulator one is vertical and the other horizontal position. The shackle insulator is round-shaped and includes a hole in the middle side for bolting. the galvanized plate is used on both sides of the shackle insulator.
Materials of Shackle insulator
porcelain materialRange of shackle insulator
>33KvApplications of Shackle insulator
- Shackle insulators are commonly used in low-voltage distribution lines to support the conductors.
- In electrical service connections, They help in maintaining the electrical isolation.
- Shackle insulators find application in telecommunication cables and wires.
- Shackle insulators are used in conjunction with guy wires and anchors in utility poles and towers.
- Shackle insulators are utilized in transformer and meter connections, providing support and insulation for the wiring and connections between transformers, meters, and overhead lines.
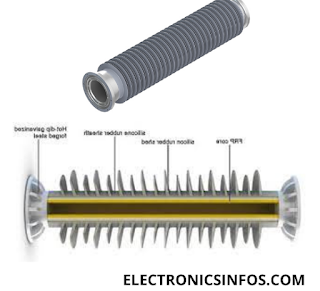
Hollow insulators
Hollow insulators are essential components in electrical systems, providing insulation and mechanical support for various types of equipment. They are made from high-strength materials like aluminous porcelain. With voltage ratings up to 800 kV and mechanical ratings up to 50 KN.
Hollow-type insulators are available in cylindrical, circular and conical shapes. Hollow insulators are components of the bushings that provide safety to transformers and circuit breakers. Hollow-type insulators are used in different positions including
- Lightning arresters.
- Power transformer bushings
- CT(current transformer)
- PT(Potential transformers)
- Capacitive voltage transformers
- Circuit breakers
 |
| Hollow Insulators |
Materials of hollow insulator
porcelain materialRange of hollow insulator
33kv up to 800kvApplications of Hollow insulator
- Hollow insulators are extensively used as transformer bushings to provide electrical insulation.
- In circuit breakers, hollow insulators serve as bushings to isolate the high-voltage components from the grounded parts.
- Hollow insulators are used in switchgear and substation equipment such as disconnect switches, voltage regulators, and capacitor banks.
- In high-voltage transmission lines, hollow insulators are used as suspension or post insulators to support overhead conductors.
- Hollow insulators are suitable for both indoor and outdoor installations.
porcelain insulators
The usage of Porcelain insulators is common in transmission and distribution systems. porcelain insulators are suitable for harsh environments. Electrical strength of the porcelain insulators is higher as compared to the other insulators. porcelain insulator surface degradation rate is low so we used a coating that provides protection against soil and contamination.
 |
| Porcelain Insulator |
Materials of Porcelain insulator
- Porcelain
- Polymer (Composite)
- Glass
- Ceramics
- feldspar
- china clay
- flint
- ball clay
- talc
Range of Porcelain insulator
Applications of Porcelain insulator
- They provide electrical insulation between the conductor and the supporting structure.
- Porcelain insulators are also used in distribution lines for medium and low-voltage electricity distribution.
- Porcelain insulators ensure a safe and reliable power supply to electric trains.
- In heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, porcelain insulators are used to support electrical components and wiring.
- Porcelain insulators are used with lightning arresters and surge arresters to provide insulation.
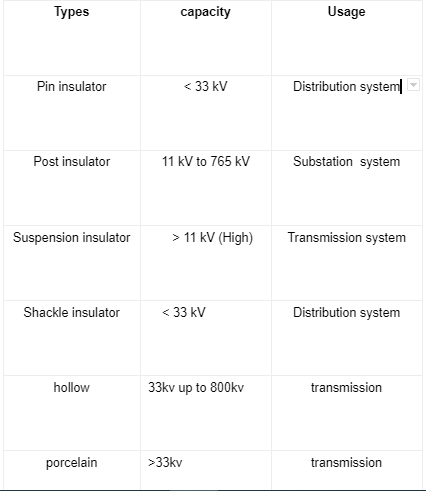
Range of Different Insulators
Factor to be considered during the selection of insulator
- thermal conductivity must below
- mechanically strength must be high
- environment friendly
- degradation level is low
- it must be fireproof
- the cost of the insulator is low
- It must be odourless
- it must be water-repellent
- the weight of the insulator is light
- combustibility level is low
- thermal conductivity is low
Insulating Materials
- plastic
- mica
- wood
- glass
- porcelain
- glass
- steatite
- polymer
- artistic
- PVC
Conclusions
Insulators play an important role in electrical systems by preventing the free flow of electricity and ensuring safety. They come in various types, each with unique properties and applications.
For instance, glass and porcelain insulators are commonly used in power transmission lines due to their durability and resistance to environmental conditions.
Rubber and plastic insulators are preferred for household and industrial wiring because of their flexibility and insulating properties. In high-voltage applications, materials like mica are used for their ability to withstand high temperatures and voltages.
Frequently Asked Questions: FAQS
What are insulators?
Why are there different types of insulators?
What are the common types of insulators?
What are suspension insulators?
When are strain insulators used?
What role do stay insulators play?
What are porcelain insulators, and where are they commonly used?
What are polymer (composite) insulators, and what are their advantages?
What are ceramic insulators, and what are their characteristics?
What factors should be considered when selecting insulators for specific applications?
What are some common standards and regulations governing the design and use of insulators in electrical systems?
Related Posts




.png)



0 Comments
please do not insert spam links