What is Arc Furnace?

An arc furnace is a type of industrial furnace that uses an electric arc to melt materials. The electric arc is generated between electrodes. when the temperature reaches the melting point of the materials it starts melting.
Arc furnaces come in various sizes, from small units for laboratory work to large industrial furnaces for mass steel production. They are also used in non-ferrous metals such as copper, aluminium, and titanium.
Arc furnaces are more efficient, have a higher production rate, and can produce higher-quality alloys.
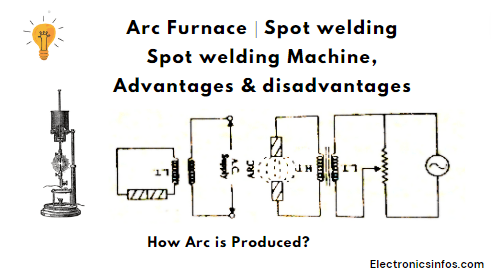
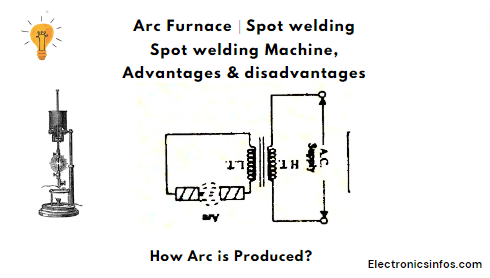
How is Arc Produced?
This occurs when a current passes through a normally nonconductive medium like air. The initiation of an arc discharge can happen through thermionic emission, where electrons are emitted from heated electrodes.
Once the arc is initiated, it can be sustained by the continuous thermionic emission of electrons.
Types Of Arc Furnace
- Direct Arc Furnace
- InDirect Arc Furnace
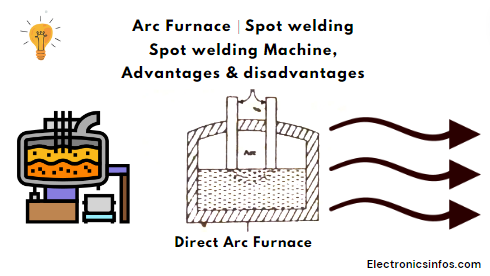
Direct Arc Furnace
This is the Direct method Of arc production When we connect a supply across the electrodes the air becomes conductive material due to ionization of air. when it's conducive the arc is produced between the electrodes. the temperature of the arc is 3000 to 3500 degrees. we used this temperature for heating purposes.to regulate the voltage we control the arc length and resistance.
we use a step-up transformer to produce high voltage. direct arc furnace is used to melt the steel. the construction of this furnace is simple. the control of a direct arc furnace is simple.
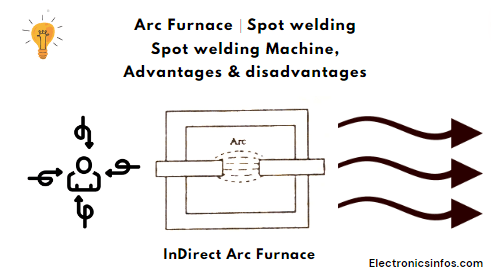
Indirect Arc Furnace
An indirect arc furnace is an arc furnace in which both electrodes are connected at the start. we give the supply with the help of a step-down transformer. when we disconnect the electrodes gradually the arc is produced between the electrodes that are dependent on the separation distance between the electrodes.
in the indirect method, the heat is transferred via the radiation method. the temperature of the indirect arc furnace is between 1500 to 2000 degrees. An indirect arc furnace is used for non-ferrous metals.
Different types of Arc welding including
- Metal inert gas Arc welding
- Shielded Metal arc welding
- induction arc furnace
- Submerged Arc welding
- plasma arc furnace
Metal inert gas Arc welding
Advantages of MIG welding
- MIG welding can be used to weld steel, stainless steel, aluminium, copper, and nickel alloys.
- It is suitable for welding both thin and thick materials.
- The continuous wire electrode and automatic feeding system contribute to increased productivity.
- The use of shielding gas in MIG welding helps create clean and slag-free welds.
- MIG welding produces less weld spatter.
- MIG welding can be performed in various welding positions, including flat, horizontal, and vertical. MIG welding produces a smaller heat-affected zone.
Shielded Metal arc welding
Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) is known as manual metal arc welding (MMA or MMAW). Shielded metal arc welding uses a consumable electrode coated with a flux to create an arc. This arc is used to join metals.
When the electrode is struck against the workpiece, an electric arc forms between the electrode and the workpiece, melting both the electrode and the base material. The flux coating on the electrode vaporizes and forms a shielding gas and slag layer, protecting the weld pool from atmospheric contamination.
Advantages of Shielded Metal Arc Welding
- it Can weld a wide range of metals.
- it is Suitable for various locations, including outdoor sites.
- The Equipment and consumables are relatively inexpensive.
- It provides deep penetration for thick materials.
- It uses flux-coated electrodes for shielding.
- it is a Stable arc even in outdoor conditions.
- it produces high-quality welds with good mechanical properties.
Induction arc furnace
An induction arc furnace uses the principle of electromagnetic induction. An induction coil surrounds the metal charge (scrap metal or raw materials), creating an alternating magnetic field.
This field induces eddy currents within the metal, generating heat due to resistance. The combination of induction heating and the electric arc rapidly heats the metal charge to melting temperatures.
Advantages of Induction arc Furnace Welding
- The combination of electromagnetic induction and the arc provides rapid and uniform heating of the metal charge.
- induction arc furnaces can be more energy-efficient.
- Induction heating provides precise control over the heating process.
- The induction heating process minimizes heat loss compared to other heating methods.
- Induction arc furnaces can handle ferrous and non-ferrous metals, alloys, and scraps.
- Induction heating produces a cleaner melting environment compared to some other heating methods.
Submerged Arc welding
Submerged Arc Welding (SAW) is a welding process that involves melting and joining metals using a continuous wire electrode. Submerged Arc Welding (SAW) is a highly efficient automated welding method.
This process is renowned for producing high-quality, uniform welds, especially over long runs, essential in heavy machinery manufacturing, shipbuilding, and pipeline construction.
Advantages of Submerged Arc Welding
- One of the most significant advantages of SAW is its high deposition rate, which can approach 45 kg/h (100 lb/h).
- Submerged Arc Welding is operated in an automatic or mechanized mode.
- The submerged arc process provides deep weld penetration.
- The use of flux in SAW minimizes spatter and spatter-related issues.
plasma arc furnace
A Plasma Arc Furnace (PAF) is an advanced type of electric arc furnace that utilizes a plasma torch to generate extremely high temperatures. A plasma arc furnace uses a plasma torch, which is an electrically conductive gas (such as argon, nitrogen, or a mixture) ionized by an electric arc.
The plasma torch generates temperatures exceeding 10,000°C. The intense heat from the plasma torch is directed onto the material to be melted. The molten material is then processed, refined, alloyed, or formed.
Advantages of Plasma Arc furnace
- PAFs can generate temperatures far higher than traditional electric arc furnaces.
- Plasma arc furnaces offer precise control over temperature.
- The concentrated heat from the plasma torch results in high energy density.
- The use of inert gases in plasma generation creates a clean melting environment.
- PAFs can be more energy-efficient due to their focused heat generation.
- Clean melting environments and reduced energy consumption.
- Plasma arc furnaces can be integrated with automation systems for enhanced process control.
Spot Welding
Spot welding is a process used to join two or more metal sheets together at localized points. Spot welding involves applying pressure and electrical current to the workpieces at specific points.
The workpieces are clamped between two electrode tips, made of copper alloys to withstand high currents and heat. When the electrodes apply pressure, an electric current passes through the workpieces, generating heat at the contact points. This causes them to melt and fuse together.
The weld is formed when the current is turned off, and the melted material solidifies, creating a strong bond.
Types of Spot Welding Machine
- Manual Spot Welders
- Semi-Automatic Spot Welders
- Automatic Spot Welders
Automatic Spot Welders
Spot welding Machine
Advantages of Spot Welding
- Spot welding is a fast process, with typical weld times ranging from fractions of a second to a few seconds.
- High-speed production can be achieved with spot welding.
- Spot welding equipment is relatively affordable compared to some other welding methods.
- Spot welding does not require additional filler material.
- The localized heat input of spot welding minimizes distortion and warping of the workpieces.
- Spot welding produces strong and durable welds.
- Spot welding produces clean welds with minimal spatter.
- Spot welding typically generates less waste compared to some other welding methods.
Disadvantages of Spot Welding
- Spot welding creates a localized heat-affected zone (HAZ) around the weld area.
- The electrodes used in spot welding can experience wear and degradation over time.
- Spot welding produces welds with limited penetration depth.
Applications of spot welding machine
- This method is used to weld the thin sheets.
- this method is used to weld the metal sheet structure.
- All boxes, enclosing cases and boxes are also welded with a spot welding machine.
Conclusions
In conclusion, spot welding offers several advantages, including speed, efficiency, cost-effectiveness, strong and clean welds, versatility, automation compatibility, and environmental benefits.
These qualities make it a preferred welding process for various industries, especially in high-volume production environments where rapid and reliable joining of metal components is essential.

.png)

-Electronicsinfos.png)

0 Comments
please do not insert spam links