What is the importance of cooling in a transformer?
Factors to consider when selecting a cooling method for transformers
- Regulatory Standards
- Transformer Type and Capacity
- Maintenance Requirements
- Environmental Conditions
- Load Variations
- Energy Efficiency
- Safety and Reliability
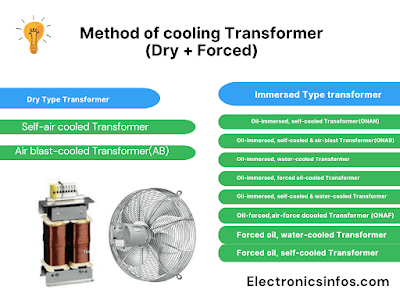
10 Method of cooling Transformer (Dry + Forced)
Dry Type Transformer
- Self-air cooled Transformer
- Air blast-cooled Transformer(AB)
Oil Immersed Type Transformer
- Oil-immersed, self-cooled Transformer(ONAN)
- Oil-immersed, self-cooled & air-blast Transformer(ONAB)
- Oil-immersed, water-cooled Transformer
- Oil-immersed, forced oil-cooled Transformer
- Oil-immersed, self-cooled & water-cooled Transformer
- Oil-forced, air-forced cooled Transformer (ONAF)
- Forced oil, water-cooled Transformer
- Forced oil, self-cooled Transformer
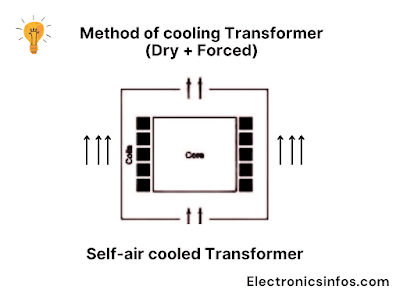
Self-air cooled Transformer(1.5MVA- 3MVA)
The capacity of a Self-air-cooled transformer is 1.5MVA to 3MVA. This type of transformer is cooled down by atmospheric air. These transformers are used in schools, hospitals, shops, shopping centres etc.
Self-air cooled transformer protects against humidity or resistance. The transformer core or coil is not enclosed in a container. The low-voltage instrument transformer is based on the self-air-cooled transformer.
Air blast-cooled Transformer(15 MVA - 35 MVA)
To Cool down the transformer, Air is circulated with the help of a blower from bottom to top is called an Air blast-cooled transformer. This type of transformer is enclosed in a metal box with a capacity between 15 MVA to 35 MVA.
Oil-immersed, self-cooled Transformer( UPto 30 MVA)
This type of transformer is also called ONAN(Oil Natural Air Natural). It's widely used because of its simple working operation. The manufacturing capacity of this type of transformer is up to 30MVA.
This type of transformer is enclosed in a metal tank in which the transformer core and windings are immersed in insulating oil. In this type of transformer oil is circulated in the transformer naturally.
The small oil-immersed self-cooled transformer surface is plane but the large transformer surface is corrugated with external tubes. we also used radiators on large-capacity transformers. The main principle of this type of transformer is the convection method.
Oil-immersed(self-cooled & air-blast)Transformer(up to 60 MVA)
Large transformers use combinations of self-cooled and air blast methods. The construction of this type of transformer is like an oil-immersed self-cooled transformer.
The main difference is just we used blowers with the main tank. This circulating air provides very fast cooling for the transformer.
The motor of the blowers is controlled with a thermostat automatic method. The thermostat on the motor circuit and operate the blowers. when the temperature reaches its normal state, the thermostat senses this temperature and turns off the motor.
Oil-immersed, water-cooled Transformer( Upto 500MVA)
Large self-cooled transformers are expensive, due to this we used an oil-immersed water-cooled method. The core and windings are totally immersed in insulating oil, but we circulate the water in the external tubes.
This type of transformer is used in the high voltage transmission lines. we prefer this method where water is available in excess quantity, and we achieve the head of water easily.
The main disadvantage of this system is we need a water tube system in the transformer. Due to the leakage of water tubes, the insulation of oil deteriorates.
Oil-immersed forced oil-cooled Transformer
In this type of method, both the core and winding of the transformer are immersed in oil. A pump is also used to circulate the oil in external tubes, For this purpose, we use a pressure system that circulates the oil in tubes to provide efficient cooling. In this method,
we also used heat exchangers like automotive radiator type which consists of oil-to-heat exchanger tubes. The pump rotates the oil quickly up to down which cools down the transformer temperature quickly.
Oil-immersed(self-cooled & water-cooled)Transformer
In this method, The core and windings are immersed in the insulating oils. This is a combination of Self-cooled and water-cooled.
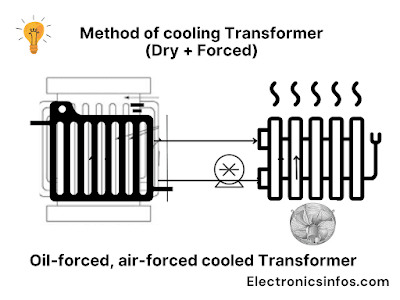
Oil-forced, air-forced cooled Transformer(OFAF)
In this method, the heat is exhausted from windings with the help of Blowers. we also use an oil pump system that circulates the oil in external tubes. This is a combination of oil-forced and air forces.
Forced oil, water-cooled Transformer
This system is used where when we use water as a coolant. we know that water has high heat conductivity and specific heat so that's why we used this method widely. in this method, we used an oil pump between the transformer and heat exchangers.
when oil enters heat exchangers the pump increases the pressure of oil in the transformer. heat exchangers are directly connected to the transformer tank.
The pressure of cooling water is less than the oil pressure in the heat exchangers. we both separate tubes for oil and water to avoid leakage mixing of water and oil.
Forced oil, self-cooled Transformer
In this method, The oil is circulated by the force. For this purpose, we used radiators so oil is easily circulated in the tubes.
Conclusion
FAQS(Frequently Ask Questions)
What is the cooling of the transformer?
Why do transformers need cooling?
What are the common methods of transformer cooling?
How does the ONAN cooling method work?
What is the role of radiators in transformer cooling?
How does forced air to improve transformer cooling?
Related
Posts :
How to Reduce The Transformer Losses?
Single Phase Transformer Vs Three Phase
Transformer
EMF Equation Of Electrical Transformer
3 Types of Electrical Transformers w.r.t
Core




.png)



0 Comments
please do not insert spam links